

Vaccines for Children in India: A Comprehensive Guide
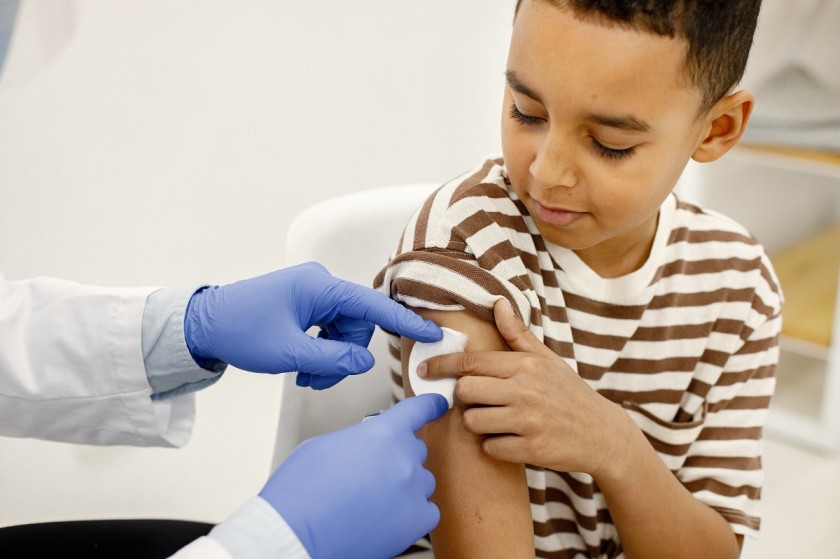
The national government is running multiple campaigns for free vaccinations for children below 12. With a vast population and diverse economic conditions present in India, vaccinations are a necessity to safeguard children from life-threatening diseases. In this piece, we will discuss the significance of vaccines, the challenges faced, and a guide to the immunization schedule.
The Importance of Vaccination
The human body has the incredible ability to fight infections and diseases on its own. However, for infants and young children, the immune system takes time to get fully developed. Vaccines work by stimulating the immune system and recognizing pathogens. Vaccines in underdeveloped children ensure that the body is prepared when faced with real infections.
Vaccinations in children help the immune system recognize the pathogen, produce antibodies, and create memory cells. These three steps ensure the child is safe and protected when encountering a real disease.
Smallpox, measles, polio, and diphtheria if widespread can cause mortality among children. For instance, in 1980 Smallpox killed several and left many with unwanted scars on the body. This was eradicated globally through a rigorous vaccination program. This achievement was a testament to the power of vaccination. Here’s why vaccinations are crucial:
Prevention
Vaccination shields infants from life-threatening, known and unknown diseases. Vaccines offer reliable protection, ensuring safety from diseases that can lead to lifelong complications.
Community Disease Protection
Getting your child vaccinated contributes to herd immunity. Herd immunity helps protect vulnerable individuals who can not be vaccinated due to age restrictions or other medical conditions. This collective effort minimizes the spread of dangerous diseases.
Safety and Effectiveness
Before coming into the market vaccines undergo extensive testing and rigorous monitoring to ensure fully covered safety and effectiveness. The benefits far outweigh any potential risks, offering essential protection against preventable illnesses.
Immunity Builder
Vaccinations teach the baby’s immune system to recognize and fight harmful pathogens, preparing them to combat future infections.
Healthy Body Development
On-time vaccination ensures a strong immune foundation in babies growing healthier. This increases the chances of optimal physical and cognitive development.
Guide to the Childhood Immunization Schedule
Childhood immunization isn’t a one-time event - it’s a planned series of doses administered by healthcare professionals and government agencies, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) & the World Health Organization (WHO). It includes the perfect intervals to maximize efficacy and help parents ensure their children are fully protected. Below shared is the list of vaccines for babies.
| Age | Vaccine |
|---|---|
| At birth | Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG), Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV), Hepatitis B bi |
| 6 Weeks | Pentavalent (1st dose), OPV (1st dose), Rotavirus (1st dose), PCV (1st dose) |
| 10 Weeks | Pentavalent (2nd dose), OPV (2nd dose), Rotavirus (2nd dose) |
| 14 Weeks | Pentavalent (3rd dose), OPV (3rd dose), Rotavirus (3rd dose), PCV (2nd dose) |
| 9-12 Months | Measles-Rubella (1st dose), PCV Booster |
| 16-24 Months | DPT Booster (1st dose), OPV Booster, Measles-Rubella (2nd dose) |
| 5-6 Years | DPT Booster (2nd dose) |
| 10 Years | TT (Tetanus Toxoid) |
Vaccine schedule for children protects early and continuously, prevents disease outbreaks, and builds strong immunity. Adherence to this timeline is crucial as the schedule shared by the professionals continues with booster doses and additional vaccines. Delays in vaccination can leave children vulnerable to infections during critical developmental stages.
Challenges Faced in Vaccination Coverage
Vaccination is one of the most effective public health measures to prevent diseases, but achieving comprehensive coverage remains a significant challenge. Despite widespread awareness campaigns and medical advancements, various barriers hinder vaccination efforts. Understanding these challenges is crucial for addressing gaps in immunization and ensuring a healthier global population.
Accessibility Issues
Many regions, especially in low-income and rural areas, struggle with inadequate access to vaccination facilities. Unreliable transport, lack of road connectivity, and internal rural areas still remain underserved. Families facing poverty issues prioritize basic necessities over healthcare services and often end up overlooking vaccinations. These issues lead to uneven immunization rates, leaving the vulnerable population of children at risk of preventable diseases.
Lack of Awareness and Education
There’s still a significant portion of the population that is uninformed about the importance of vaccines and its importance. Due to the lack of awareness and education, there are several myths and misinformation about vaccines causing severe side effects in children. Surprisingly, a few of the communities have cultural and religious practices, and their beliefs conflict with immunization programs.
Political and Economic Instability
Political conflicts, economic crises, and war-torn regions create significant challenges for vaccination programs. Refugees and internally displaced populations often lack access to consistent healthcare. Additionally, economic instability reduces investments in healthcare infrastructure and vaccination campaigns.
Vaccine Hesitancy
Even in areas where vaccines are readily available, several individuals hesitate to get vaccinated due to fear. The origin of this fear is again the lack of awareness and exposure to education. There’s a lack of trust in the healthcare system, government, and pharmaceutical companies.
Government Initiatives to Improve Vaccination Rates
Government policies play a crucial role in improving vaccination rates, ensuring each individual is protected from preventable diseases. These initiatives are aimed to address accessibility, awareness, and affordability, making vaccine schedules for children more effective. Below is an overview of the strategies started by the government to enhance vaccination rates.
Universal Immunization Programme (UIP)
In the year 1985, UIP the Universal Immunization Programme launched one of India’s flagship healthcare initiatives.
- It offers free vaccines against life-threatening diseases like polio, measles, tetanus, and hepatitis B.
- Gradually, the program added newer vaccines covering other diseases such as rotavirus, pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV), and measles-rubella.
- The launch of UIP strengthened the cold chain systems and logistics ensuring vaccine efficacy across the country.
Mission Indradhanush
Aimed at serving pregnant women and children under two years of age who missed routine vaccines, Mission Indradhanush was launched in 2014.
- The initiative is focused on underserved populations, urban slums, tribal populations, and conflict zones.
- To widen the coverage, this mission was relaunched in 2017 as Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI). This was launched to cover high-priority districts, ensuring a 90% immunization rate.
- Door-to-door campaigns and mobile vaccination teams ensure outreach to marginalized communities.
Pulse Polio Campaign
Started in 1995, the Pulse Polio Immunization Program was instrumental in eradicating polio from India.
- A mass vaccine schedule for babies is held nationwide on polio vaccination days. It involves millions of healthcare workers and volunteers.
- Considering the booth location polio drops are administered in schools, religious places, community centers, and other outreach areas ensuring to reach every child.
- Continuous surveillance ensures no missed cases, even in remote regions.
- Pridefully, India achieved polio-free status in 2014, marking a historic name in the public health milestone.
Digital Platforms
Electronic Vaccine Network the eVIN system, introduced in 2015, leverages technology to strengthen immunization logistics.
- It offers real-time tracking and monitors vaccine stocks, temperature, and delivery systems to minimize wastage and ensure efficiency.
- Digital solutions facilitate data-driven decision-making for vaccine distribution planning.
- Surprisingly, the eVIN system has been adopted in all states and union territories, enhancing the UIP’s operational efficiency.
Conclusion
The importance of vaccination for children in India cannot be overstated. Vaccines are more than just medical interventions. They work as a testament to human ingenuity and a powerful symbol of our commitment to a healthier India. At Promhex Multi Speciality Hospital we are dedicated to providing the finest healthcare services and delivering superior care.
Vaccinations are a cornerstone of preventive healthcare. It helps in safeguarding individual lives and strengthening public health systems. As we plan and move forward into the future, the importance of continued investments in immunization programs, public education, and equitable healthcare access will be crucial for achieving universal vaccination coverage. Need more support? Connect with professionals at Promhex Multispeciality Hospital now.
Go Back
24 x 7
We’re Open
Our Specialities

#promhexspecialities
Promhex a multi-speciality hospital has a strong presence in Greater Noida. We have the best team of doctors and staff here, who believe in providing best healthcare services at affordable cost.
 Announcement
Announcement 



 ORDER MEDICINE
ORDER MEDICINE









